Azithromycin
Azithromycin
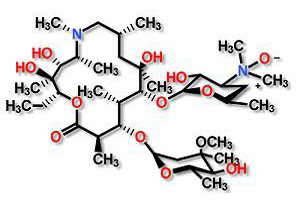 Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler's diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections.
Azithromycin is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes middle ear infections, strep throat, pneumonia, traveler's diarrhea, and certain other intestinal infections.
 Calcium D Pantothenate
Calcium D Pantothenate
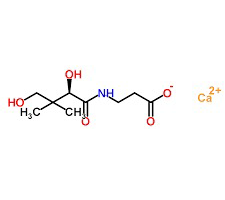 Pantothenic acid, also called pantothenate or vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin. Pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient. Animals require pantothenic acid to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Pantothenic acid, also called pantothenate or vitamin B5 (a B vitamin), is a water-soluble vitamin. Pantothenic acid is an essential nutrient. Animals require pantothenic acid to synthesize coenzyme-A (CoA), as well as to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
 Cefoperazone
Cefoperazone
 Cefoperazone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid. It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating Pseudomonas bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics.
Cefoperazone is a third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic, marketed by Pfizer under the name Cefobid. It is one of few cephalosporin antibiotics effective in treating Pseudomonas bacterial infections which are otherwise resistant to these antibiotics.
 Doxycycline HCL
Doxycycline HCL
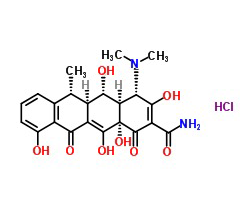 In addition to the general indications for all members of the tetracycline antibiotics group, doxycycline is frequently used to treat Lyme disease, chronic prostatitis, sinusitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, acne, rosacea, and rickettsial infections.
In addition to the general indications for all members of the tetracycline antibiotics group, doxycycline is frequently used to treat Lyme disease, chronic prostatitis, sinusitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, acne, rosacea, and rickettsial infections.
 Gentamicin Sulphate BP
Gentamicin Sulphate BP
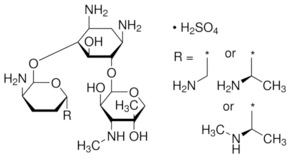 Gentamicin, sold under brand names Garamycin among others, is an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class, used to treat several types of bacterial infections.[1] This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis among others. It is not effective for gonorrhea or chlamydia infections. It can be given intravenously, by injection into a muscle, or topically.[1] Topical formulations may be used in burns or for infections of the outside of the eye.[2] In the developed world it is often only used for two days until bacterial cultures determine what antibiotics the infection is sensitive to.[3] The dose required should be monitored by blood testing.[1]
Gentamicin, sold under brand names Garamycin among others, is an antibiotic of the aminoglycoside class, used to treat several types of bacterial infections.[1] This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis among others. It is not effective for gonorrhea or chlamydia infections. It can be given intravenously, by injection into a muscle, or topically.[1] Topical formulations may be used in burns or for infections of the outside of the eye.[2] In the developed world it is often only used for two days until bacterial cultures determine what antibiotics the infection is sensitive to.[3] The dose required should be monitored by blood testing.[1]
 Oxytetracycline HCL
Oxytetracycline HCL
 Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, active against a wide variety of bacteria. However, some strains of bacteria have developed resistance to this antibiotic, which has reduced its effectiveness for treating some types of infections.
Oxytetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, active against a wide variety of bacteria. However, some strains of bacteria have developed resistance to this antibiotic, which has reduced its effectiveness for treating some types of infections.
 Norfloxacin
Norfloxacin
 Norfloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic antibacterial agent occasionally used to treat common as well as complicated urinary tract infections. It is sold under various brand names with the most common being Noroxin
Norfloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic antibacterial agent occasionally used to treat common as well as complicated urinary tract infections. It is sold under various brand names with the most common being Noroxin
 Piracetam
Piracetam
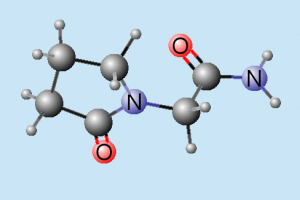 Piracetam is a nootropic drug in the racetams group, with chemical name 2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide. It shares the same 2-oxo-pyrrolidone base structure with pyroglutamic acid. Piracetam is a cyclic derivative of GABA.
Piracetam is a nootropic drug in the racetams group, with chemical name 2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide. It shares the same 2-oxo-pyrrolidone base structure with pyroglutamic acid. Piracetam is a cyclic derivative of GABA.
 Sulbactam
Sulbactam
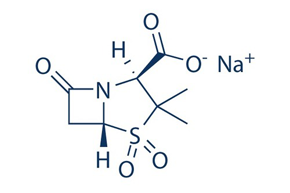 Sulbactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor. This drug is given in combination with β-lactam antibiotics to inhibit β-lactamase, an enzyme produced by bacteria that destroys the antibiotics
Sulbactam is a β-lactamase inhibitor. This drug is given in combination with β-lactam antibiotics to inhibit β-lactamase, an enzyme produced by bacteria that destroys the antibiotics
 Tranexamic Acid
Tranexamic Acid
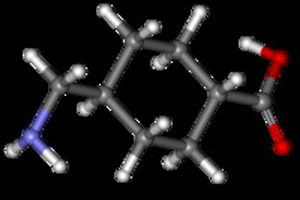 Tranexamic acid is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from trauma, surgery, and in various medical conditions including hemophilia and heavy menstrual bleeding. It comes in oral and intravenous forms
Tranexamic acid is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from trauma, surgery, and in various medical conditions including hemophilia and heavy menstrual bleeding. It comes in oral and intravenous forms
 Mannitol Dc Grade
Mannitol Dc Grade
 Mannitol, also known as mannite or manna sugar,[1] is a white, crystalline solid that looks and tastes sweet like sucrose.[2] Medically it is used to treat increased intracranial pressure.[3] It also has several industrial uses. In plants its purpose is to alleviate osmotic stress.
Mannitol, also known as mannite or manna sugar,[1] is a white, crystalline solid that looks and tastes sweet like sucrose.[2] Medically it is used to treat increased intracranial pressure.[3] It also has several industrial uses. In plants its purpose is to alleviate osmotic stress.